Canker Sores vs. Cold Sores - what’s the difference?
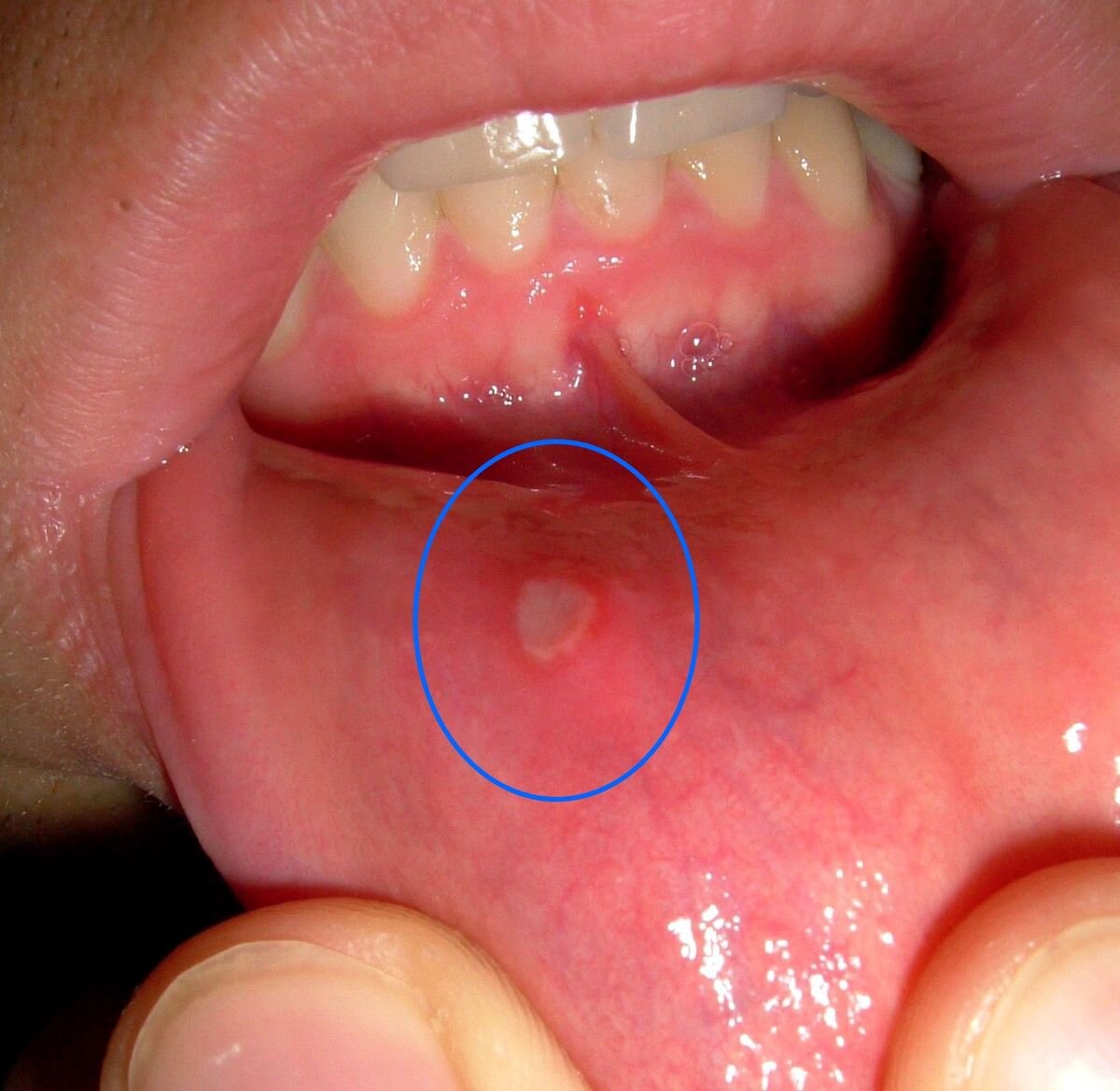
/Canker sores (or called apthous ulcers) are a shallow lesion that develops inside the mouth on soft tissues, such as the cheeks, below the gums, inside of the lip, under the tongue or on the tongue. They look like a small white or yellow circle with a red border. They can burn or cause discomfort when you eat, drink or even when you brush your teeth. Canker sores do not occur on the outer surface of the lips and are NOT contagious. They are quite common and the exact cause is unknown, but they are not known to be a viral nor a bacterial infection. Possible triggers are:
stress,
acidic foods,
trauma such as biting the cheek, sports injury or brushing too hard,
ingredients in mouth products such as sodium lauryl sulfate,
diet lacking in vitamin B12, zinc, folate (folic acid) or iron,
hormonal shifts during menstruation
Most of the ulcers resolve on their own in 2 weeks. Applying a topical numbing gel can help with discomfort for children that are old enough for it. It is recommended to avoid spicy or acidic foods while the healing is in progress. Use a soft bristled toothbrush when brushing the teeth twice daily. Avoid toothpastes and mouth rinses that contain sodium lauryl sulfate.
Cold sores (or called fever blisters), however, usually appear outside the mouth on or around the lip. They usually look like a cluster of blisters, and they can eventually burst, causing oozing and crusting. Cold sores result directly from the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). This virus is dormant until triggered, which is when you might experience a tingling or burning sensation in your mouth and the development of a sore. Several factors can trigger the recurrence of a cold sore:
Stress
Other viral infections
Fatigue
Exposure to sun or wind
Hormonal changes
Fever
Cold sores usually heal on their own but may take up to 2-4 weeks. Because cold sores are caused by HSV-1, they may be treated with an antiviral topical, blister treatment or oral medications if they do not heal on their own. The virus itself cannot be cured. The American Academy of Dermatology strongly encourages the use of sunscreen during an outbreak, as sun exposure can affect the healing of the sore. Unlike canker sores, cold sores ARE contagious and can spread easily, so to prevent spreading the virus, you should not share utensils or any other items that touch the mouth, and avoid kissing.
Dr. Lindhorst and Dr. Theriot are happy to address any questions or concerns. Please don’t hesitate to give us a call at (713) 861-4000.